Constitution & Dynamics of Dark Matter ... Continued
The Physics of Reality
We are on page 23, and from here onwards, we will be able to make real progress. The reason, is simple: to destroy the false scientific narrative about the origin and development of the universe, one does not have to waste time, thinking of counter-arguments. All one has to do, is to take seriously, what scientists are claiming to be true, lay it out, in its illogical detail, and then proceed to use empirical evidence, and observational data to expose its internal contradictions. Since we have used the first 22 pages of this blog to logically lay out, all the laws that such evidence is a manifestation of, it is merely a matter of procedure and time, for us to now use those laws incisively, to interrogate the unfounded claims of popular science - also known as Scientism. It is with that aim, that we will now proceed to outline, in thorough detail, the many unfounded assertions of the Big Bang theory. This theory, as we learnt in our last section, forms the standard model of cosmology, that is, it the theory most widely supported by scientists to be the accurate description of how the universe came to be. It is alternately, called lambdaCDM, and incorporates the failed ideas of the cosmological principle: Isotropy and Homogeneity. We have shown that both, these ideas are at odds with, and in fact disproven by the facts, by experiment, and by all observational data. Hence, the lambda term, in lambdaCDM, has been falsified. However, as we have also established, Dark Matter, is a thing, and in fact, it is the MAIN thing, in the universe. Whatever the true character of the universe is, it is founded on, and thus more closely aligned with dark matter, than it is with normal, baryonic, physical matter.
Scientists tried to hitch their own creation - dark energy: as expressed by the symbols of lambda, or the cosmological constant - into the realm, of the scaffolding of the universe: dark matter, by co-branding both entities under the same DARK umbrella, but to no avail. In reality, the two entities, have nothing to do with each, despite a naming convention that eschews the facts, and promotes obfuscation through a tiresome, baseless cross-branding exercise. Like Maxwell, trying to attribute the properties of electromagnetic radiation to the ether, such false formulations, will always garner null results! I pray, that you did not miss the irony, that the results of the Dark Energy Survey of the universe, was the largest ever distribution of Dark Matter! Take the time to discern, what that signifies. Indeed, between dark energy, and dark matter: only one is a reality, the other - just a figment of intellectual imagination! An unfounded flight of fancy for which there is no future.
To advance our task, we will deepen our knowledge of, then employ the salient features of the universe that we have already learned about, using their uncontroversial, universally accepted features to expose and invalidate, any and all falsehoods. In our quiver, we have the Mighty CMB, Dark Matter, the widely published theory of Big Bang cosmology, galactic redshift, and the critical density of the universe. And, in the other corner we have intellectual hubris and metaphysics! Yes, you read that correctly: the published theory of Big Bang cosmology is on the side of the Bible. That's because, the only way to remove all wiggle room from your opponent's stance, is to have them state their case, as clearly and unambiguously as possible - publicly and in writing. In the case of the Big Bang, there are volumes and volumes of written material. Then, you only have to wait until the evidence has accumulated to be able to interrogate their case - in their own words - against the truth. One easy way to falsify such errant claims is to then accept the assertions of one's opponents as truth, and then falsify them by proving their internal contradictions. As it relates to Big Bang Cosmology, Scientism has held sway for so long over the scientific community, that its supporters have freely championed the claims of Big Bang cosmology for decades! all but sure, that a reckoning with reality would be the one thing, that they would never have to face. But truth doesn't work that way. If only they had known. The Achilles heal of ALL falsehoods, and scientism, is that in the end truth will always reign. Scientism depends on ethers to advance its ideas. This works wonderfully, in the beginning, as there is an absence of evidence, which suits the Etherists just fine, as they are then free to assign all sorts of magical functionalities to their ethers. An added bonus, being that, in the absence of empirical data, the minds of men are easily twisted toward error, for the benefits of such errors are immediate, and their consequences distant. Such developments appeal to the senses, not to reason, and are thus readily acceptable to most men. Error becomes an utilitarian, network effect:
There is no opinion, however absurd, which men will not readily embrace as soon as they can be brought to the conviction that it is generally adopted" Arthur Schopenhauer
Subir Sarkar said something very pertinent, about when, the seeds of the cosmological principle were sown and the environment, under which the Big Bang was devised, promoted and accepted:
So, the bottom line in my opinion, is that this concordance is partly manufactured, and more to the point: it rests on the underlying assumption of a cosmological model, that had its roots a century ago, and which is very difficult to modify, because ultimately, as you know well, exact solutions to Einstein's equations are very hard to find. Except, in very highly symmetric situations. So, this model was constructed, when there was no data...." Subir Sarkar (35:28 - 36:23)
This shortsighted focus is a telltale sign of scientism and its commitment to ethers. That is precisely, the great allure of ethers! They always emerge under conditions where verifiable facts are scarce and far in between. Hence, their promoters have a blank canvass onto which they can project any reality they wish, together with a gullible public. As the ether gets more and more entrenched, as an idea, any hard to understand phenomenon, are always explained away through some function of the ether, itself. For a limited time, any debate that may ensue, is easily swatted away, as in the absence of evidence, opinions have as much weight, as reasoned explanations, since the fact that nothing can be proven factually, also means nothing can be falsified! However, once evidence does begin to be compiled - the cracks start to show, and the etherists start their inevitable backpedaling: eventually, the tables turn! Now, the very dynamics that gave etherists, freedom from facts, become their Achilles heel, as they are forced to try and reconcile their unfounded theories, with the facts, as borne out by observable data. Such is the case, with the standard model of cosmology - the Big Bang theory, its concordance model, and the two unfounded assumptions that are at its foundation: Isotropy and Homogeneity. The Big Bang model of the universe, is more formally referred to as ACDM (lambdaCDM).
So that we are later able to carefully and precisely take it apart claim by claim, we will now define and describe Big Bang Cosmology, as it appears in published detail - for, over the years of its popularity, it has been published and republished endlessly, by its many, many popular scientific backers.
Big Bang Cosmology & the Expansion of the Universe
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model explaining the existence of the observable universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale evolution. The model, describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature.... Crucially, the theory is compatible with Hubble–Lemaître law — the observation that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away from Earth. Extrapolating this cosmic expansion backwards in time using the known laws of physics, the theory describes an increasingly concentrated cosmos preceded by a singularity in which space and time lose meaning (typically named 'the Big Bang singularity'). Detailed measurements of the expansion rate of the universe place the Big Bang singularity at around 13.8 billion years ago, which is thus considered the age of the universe. After its initial expansion, an event that is by itself often called "the Big Bang", the universe cooled sufficiently to allow the formation of subatomic particles, and later atoms. Giant clouds of these primordial elements — mostly hydrogen, with some helium and lithium — later coalesced through gravity, forming early stars and galaxies, the descendants of which are visible today" Big Bang Article - Wikipedia
We can learn much about the fault lines inherent in the standard model of cosmology, merely, by paying close attention to its claims. In the first two sentences alone, we learn that: 1) the Big Bang supposedly explains, the existence of the observable universe from the "earliest known periods," from before the existence of the CMB. This is patently false: for, we know, that the farthest back, humankind can possibly know anything, about the universe, would relate to the appearance of the CMB: for everything we know about the universe, we learn through light. And, the CMB is the earliest known light, to have ever existed. In reality, that means we cannot know anything about the Big Bang - even in principle - because, the CMB is supposed to have appeared upto 400 000 years, after the Big Bang according to cosmologists. 2) The prevailing cosmological model, claims to prove that the mechanism, by which the universe went from its initial size to its current size was Cosmic evolution. This is a claim, we will soon easily and quickly falsify. 3) Critically, this evolutionary process expanded, the universe, which is a key word in the claim, because it presupposes, that everything expanded together, over time. Again, easily falsifiable by observed data. After, the first two sentences, the article continues to make false claim, after false claim, including: 4) Big Bang cosmology, is founded on extrapolating, from this claimed expansion, of the universe and by running it "backwards, in time, using the known laws of physics," we are supposed to arrive at the inescapable conclusion of the Georges Lemaitre's "primeval atom" 5) Running the extrapolation "backwards," then yields the result, of an "increasingly concentrated cosmos," one in which, the initial state had an infinitely "high density and temperature." In this scenario, all Space, matter and time fit into one point called the 'Big Bang singularity,' a state equivalent to the aforementioned "primeval atom." Simplistic, I know, but that is the claim! 6) It was only "after" the initial expansion of the universe, from this infinite density, infinite temperature point, "an event that is by itself often called 'the Big Bang,' that the universe cooled sufficiently to allow the formation of subatomic particles, and later atoms." 7) Giant clouds of these primordial elements - mostly hydrogen, with some helium and lithium, "later coalesced through gravity, forming early stars and galaxies, the descendants of which are visible today." Hence, while the structures that we see today, were not in existence in the early universe, the material from which they were later made, was in abundant supply! That too is a critically important point - for reasons we will soon, appreciate more clearly.
And, so it is, that we have 7 unambiguous claims about how the universe came to be, as per the strong assertions, of Big Bang Cosmology. It is now a straightforward issue to interrogate these claims against the proven laws of Physics, and 9 decades of empirical data and observational facts! If any of the 7 clearly stated unambiguous assertions of Big Bang Cosmology, falter, when viewed through the laws of Physics, empirical evidence, or observed data: they are FALSE! That much is clear. If the assertions, are upheld by the proven empirical laws of Physics, empirical facts and observed data, then they stand as verified, having been successfully established by the by the most rigorous tests of all! Next, then, we must go through the relevant laws, considering only the ones, which have a bearing on the validity of these claims. Again, in our corner, along with the outlandish claims themselves, we have the laws of Spectroscopy; the 4 laws of Thermodynamics; the Ideal Gas law; Newton's laws of Gravity; together with the greatest asset on our side: the Mighty CMB! In much, the same way that the Celestial Sphere, proved definitive in falsifying Homogeneity, it is crucial in understanding why all 7 claims, listed above are - incorrect. To underscore why it is so important, we will once again highlight, that all the knowledge we possess about the universe, we have gleaned, by studying light! And if we'd like to learn about the earliest history of the universe, it only makes sense, that we would, then study, the earliest light - the Mighty CMB. The following conversation between Lawrence Robert Kuhn of Closer to Truth fame, and Wendy Freedman, helps to illustrate the point:
LRK: When we look at the universe, what do we literally see?
WF: When we use our telescopes, to look back in the universe, we can see as far back as light has had time to travel to us over the intervening time. So, we know the universe is 13.7 billion years old. We can see back to a volume with a radius that's defined by the light travel time and the age of the universe. So, in effect, we can see a volume that is encompassed by 13.7 billion light years.
LRK: That 13.7 or close to that, being the radius of of a volume of a circle - big sphere - that has a radius of 13.7 billion [light] years.
WF: Yes. Now, there may be way more beyond that, but we can't actually see it!
LRK: So, anybody can theorize what they want, and maybe some of the theories are very good, but in terms of the hard core reality of what we can really see, and what we really know, that's the sphere: radius 13.7 billion [lightyears]!
WF: That's right!
Of course, the observable universe does have a Celestial Sphere, as we have already established: the Celestial Sphere, is the CMB! Hence, we can know nothing of what came before the CMB! For this reason, we know that every description of the so-called Big Bang, is a flight of fancy, a work of vivid imaginations, as it is trying to describe a time before, the first light! Hence Kuhn concludes: "So, anybody can theorize what they want ... but in terms of the hard core reality of what we can really see, and what we really know, that's the Sphere."
Having, jogged our memories to re-establish this important point, we now move on to learning exactly what the CMB, teaches us about the earliest known moments of our universe. We start first with an important quote about the Cosmic Microwave Background, from Paul Davies, esteemed physicist and prolific writer on matters scientific, currently a professor at Arizona State University. Questioned by Robert Kuhn about important breakthroughs in science, particularly those accomplished by himself, Davies details his contributions, into understanding, the one way nature of the arrow of time:
A very early one [contribution], goes under the title of the arrow of time. So, this is the familiar experience of the future and the past, are very different from each other. But pinning down, exactly what the source of that difference is, turns out to be remarkably difficult. And I was inspired by a lecture by the British cosmologist Fred Hoyle ... and he was talking about how Maxwell's equations, which describe the propagation of light and electromagnetic waves generally, say like radio waves, are symmetric in time. And yet, of course, we all know, that when we tune into a tv show, we're receiving the show a little bit after it was transmitted, never a little bit before. And yet, according to the equations, everything should work forwards and backwards in the same way, so what is it that breaks that symmetry? And it was, was and still remains, a contentious issue. But I like to think that I myself, made a contribution to pulling that field together. It turns out, that you can trace the origin of this arrow of time, back to the origin of the universe. That the universe was set up - we don't know how - in a rather special state!" Paul Davies (2:04 - 3:15)
Where, according to all you have thus far learnt, would we search for information about this rather special state, that the universe was set up in? A secondary question is: what is the significance of this "rather special state?" We attack the former question, first. By now, you should know - without hesitation - that the answers are provided only by studying light. As the facts stand, at this time in the development of the universe, there are no stars, hence the only light we can consult is the Mighty CMB.
Before we go in-depth into our rebuttals, let me provide you with a short step-by-step guide of how scientists claim the universe developed: together with an accompanying Info-graphic, that outlines such claims - visually, Info-graphic 1. In doing so, I will only list the names of the major stages, called Epochs, by the scientific community. You will find them labeled on the info-graphic. They are: 1) Quantum Fluctuations cause the Big Bang; 2) Inflation; 3) CMB is produced; 4) Dark Ages: the amount of time between when the CMB appeared and the first stars evolved; 5) First Stars evolve, about 400 million years after the Big Bang, and 399 600 000 years after the CMB appeared. This last period is supposed to have lasted for more than 13 billion years, and supposedly still ongoing, and lastly; 6) the Dark Energy Epoch, or the Accelerated Expansion of the universe. If you should ever have need, to review these epochs, and the graph that illustrates their order, please refer back to this section. For now, we move forward, with the details of cosmology's claims - and how they stack up against the actual evidence.
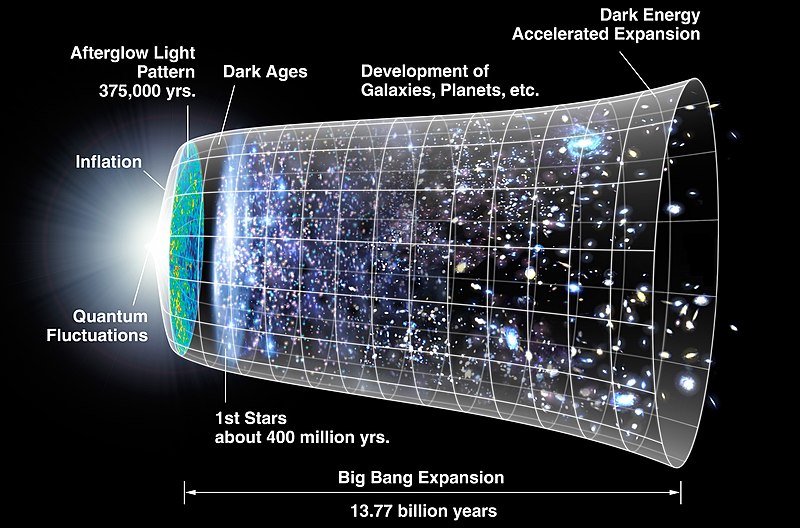
According to the Big Bang theory, the CMB, is supposed to be a relic light from the Big Bang itself. However, it was supposedly only released 380 000 to 400 000 years after, the Big Bang. This is because, that was how long it took, for the extremely hot, soup-like ionized plasma, that constituted the universe, to cool down to 3 000 Kelvin. This cooling of the universe was caused by its rapid inflation, as it entered its Inflationary Epoch. At this point, of inflationary expansion, the universe went from being opaque, and became transparent! Basically, this means, no one could see anything while it was opaque, because light was married to matter, and couldn't travel very far without interacting with ionized subatomic particles. However, once the universe was transparent, the relic light of the Big Bang, having now been decoupled (divorced), from matter, could start to freely stream through the universe. Below, I include a descriptive quote, from another esteemed Nobel prize winner, Jim Peebles. You'll be happy to know that Peebles is, the same man who came up with the Cold Dark Matter (CDM), model of the universe. In subsequent papers he married that idea to Einstein's Cosmological Constant, giving birth to the theory in its current form: ACMD. He is a man who found himself at the intersection of much of cosmological history, and activity, having carried out his Doctoral thesis under his mentor at Princeton, Robert Dicke, of CMB co-discovery fame! Peebles is the Albert Einstein Professor in Science, Emeritus, at the same revered institution - Princeton University. He is arguably, the scientist who more than any other, has had the largest influence on how people think about the early universe and its large scale structure. Below, a quote establishing his bona fides in cosmology from the Academy that awards the Nobel prize:
This year’s prize goes to contributions to our understanding of the evolution of our universe and Earth’s place in the cosmos ... James Peebles took on the cosmos, with its billions of galaxies and galaxy clusters. His theoretical framework, developed over two decades, is the foundation of our modern understanding of the universe’s history, from the Big Bang to the present day" Goran K Hansson - Secretary General of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences
So it is to him, I now turn, to define the scientific view of the very early universe: the moment in time, when the CMB, first emerged! The description comes from a talk he gave in 2015 about the progress made through 50 years of knowing about the CMB. In it, he uses a graphic entitled: Selected Measurements of CMB Spectrum (time stamp: @ 24:44), and explains:
Here's the state of the measurements today. This solid line near the top is not a theory: that's a measurement of spectacular precision. Here, are other measurements. Notice, the long range of frequencies, the theoretical curve you can just make out, running well through the observations. A glorious piece of evidence: I would say an iconic piece that shows tangibly, that the universe, had to have evolved from a different state. Because, this [the CMB spectrum] is a thermal spectrum. Our universe, as it is now, is transparent to this radiation. There's no way it could force the radiation to relax to this thermal equilibrium. The universe had to have evolved from a state in which it was dense and hot enough to have relaxed to equilibrium and then expanded away from it" Jim Peebles | UW Video - 50 Years of the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation: What We Have Learned, What Questions Remain (24:41 - 25:26)
The gist of the above quote, is that the CMB is a thermal spectrum. And that, since, it is a thermal spectrum, it must have been produced by a universe, which was in an initial state which "was dense and hot enough to have relaxed to equilibrium." In other words, a state VERY different, from the transparent one, the universe now possesses. For if the universe wasn't, dense and extremely hot, how could you explain it reaching thermal equilibrium as evidenced, by the CMB spectrum? To further clarify Professor Peebles' point, we will add weight to his argument, by again quoting from the 'same what's app group' of ideas of Davies:
When you think about the early universe, you think about the cosmic background heat radiation. And that radiation turns out to be very very close, to what we call thermodynamic equilibrium. That is, to say, if we could magically go back to the very early stages after the Big Bang, we would find there would just be uniform temperature throughout. No variation. Everything settled down into equilibrium. But the distinctive feature of the universe today, is it's very far from equilibrium! We've got a hot Sun, and gold space, for example, and that drives almost all of the processes that are asymmetric in time, on the earth's surface. So how do we get to disequilibrium, from equilibrium?" Paul Davies (3:39 - 4:19)
Before, we continue, it is important to clarify a misleading statement. The CMB is not "very, very close to ... thermodynamic equilibrium," it is: at perfect thermodynamic equilibrium! You can tell that from the professors own next words, barely a sentence afterward, when he describes the conditions the CMB was a measurement of, as: "uniform temperature throughout. No variation. Everything settled down into equilibrium."
It is also important to prepare our minds for the detective work that comes next! You must be aware that what we are doing is more than simply unraveling, the mysteries of existence. If you held that naive view, you would always be flustered by why, we often go into so much detail. The reason is simple, not only must we uncover the truth, but we must also expose the lies. This calls for an added layer of reporting and analysis. Our task is more complicated, than merely telling the truth, due to the fact that, there are many influential thinkers, whose main aim, is to cloud the waters of understanding and make them as murky and impenetrable as possible. To that end, there are no shortage of alternate explanations for how the universe came to be. I call them alternate explanations, because, in reality, there can only be one true explanation: everything else, will be shown to be failed descriptions, and ill-conceived attempts at clouding the issue. In tackling these lies, we recall our earlier discovery about the nested definitions of Cosmology, and Metaphysics. Metaphysics: was an "A priori speculation upon questions that are unanswerable to scientific observation, analysis, or experiment."*(Wordnik) More importantly, the definition of Cosmology, was nested within the one for Metaphysics. For "Cosmology," is defined as 1) "a branch of metaphysics that deals with the nature of the universe" and 2) "a branch of astronomy that deals with the origin, structure, and space-time relationships of the universe." Put simply: Cosmology, is a first of all, a branch of metaphysics, i.e. not answerable to science; and then, only secondly, is it a branch of a recognized science - astronomy. It should be obvious to everyone reading this blog, that there is no tree in existence, that could possess those two branches simultaneously! Another way to say that, is that, you cannot reconcile physics, with metaphysics. It was for good reason that Sir Isaac Newton warned,
Physics, beware of metaphysicsSir Isaac Newton
In our detective work then, you will note how we have to painstakenly, wrest the Metaphysics, out from the data. Why is that so? Remember, that metaphysics is an "A priori speculation...." That phrase "a priori," has two meanings, the first is deductive, and the second, is presumptive. Deductive reasoning is one based on "self-evident propositions" or "presupposed by experience."*(MW) While, being presumptive means: "being without examination or analysis," or b) "formed or conceived beforehand." IS THAT NOT SHOCKING? Cosmology, the science, which is supposed to underpin our whole understanding of reality, of everything from how the universe came into existence, to how we got here, and are there aliens? is effectively, a ponzi scheme: all those tax dollars invested into getting the answers, and humanity has nothing to show for it, except the hot soup mess of Big Bang Cosmology. It is obvious, that as it pertains to Cosmology, no "speculations" that are formed, fit the deductive meaning of "a priori." Since, no human was then alive, none of us can use "experience," in coming to grips with our understanding of the history of the world. That only leaves empty-headed, presumptive reasoning, which again, is defined as, " a) being without examination or analysis b) formed or conceived beforehand." Is such a conclusion on Cosmology fair? Can it really be said that an entire science is nothing but empty speculation formed beforehand? Absolutely. Surbir Sarkar plainly admitted as much:
So, the bottom line in my opinion, is that this concordance is partly manufactured, and more to the point: it rests on the underlying assumption of a cosmological model, that had its roots a century ago, and which is very difficult to modify, because ultimately, as you know well, exact solutions to Einstein's equations are very hard to find. Except, in very highly symmetric situations. So, this model was constructed, when there was no data" Subir Sarkar
It would be one thing if we were to now cross-examine the great Jim Peebles' claims against the evidence that has piled up in the course of the nine decades, that have elapsed since the Georges Lemaitre published his Big Bang theory in Nature, in 1931. But the failings of Cosmology are so fundamental, that even without evidence, they should never have seen the light of day - for they go against the then known laws of physics! Case in point, the Peebles' assertion that flies in the face of known physical laws: that the CMB spectrum had "relaxed to thermal equilibrium." Understanding why, requires that we get a thorough grasp of the "special state," that the universe was in, at the point the CMB first appeared. To help us tease that out, we will call on one of the 3 patriarchs of inflationary theory, Paul Steinhardt. Inflationary theory, is of course the concept that describes the inflationary epoch, that is supposed to have immediately followed the Big Bang, and preceded the CMB. Steinhardt, who helped lay out the groundwork for the theory, has in recent times become a staunch critic, proving convincingly that inflationary theory, is as far as you can imagine from what must have actually taken place. In a May, 2021 talk that he gave for Simon's Foundation Lectures, entitled "Time to Take the 'Big Bang' out of the Big Bang Theory?" he discusses in great detail, the "rather special state," that the universe was in at the appearance of the CMB, as mentioned earlier, by Paul Davies. I will quote the relevant parts of his discussion, then show how they, and fundamental Physics, disprove Jim Peebles' earlier statements. We start, with Steinhardt's initial thoughts on the "salient features of the universe," as reflected in the CMB.
The iconic image ... is the one that's shown here. What it's supposed to represent, is a surface around us, at great distances, far beyond the stars and galaxies. So, imagine that spherical surface ... that's what we're making an image of. And then, we're projecting it on an oval, much like we do when we're projecting the surface of the earth, on an oval in order to present it in flat two-dimensional map. So this represents the entire sky, projected into this oval. Imagine us sitting in the middle." Paul Steinhardt
So far, Steinhardt has just explained why the shape of the CMB, takes that familiar oval shape: its a 2-dimensional projection of a 3-D reality. He also outlines our empirical place within this map - all observational data, says we are in the middle of the Celestial Sphere. Below, he continues with further important details and explanations,
The red and blue colorations in the map are false colour, added to the map, to represent the variations in temperature and density at this very early stage, this infant stage of the universe. They represent variations in temperature of less than 0.01 percent. Very tiny variations .... For what we're going to talk about today, what we really want to do is focus on the same picture, but with slightly lower resolution. And the striking thing that one gets, if one reduces the resolution by just a little bit, is the first approximation" Paul Steinhardt
Those colorations are tiny variations on either side of a mean temperature. For instance the blue in the above image represents 0.0001 kelvin colder than the core temperature, and the red, 0.0001 kelvin warmer than the core temperature. The value of the first approximation is to take both sides, warmer and cooler, out of the equation, and leave the CMB as it was when it first appeared: before, whatever caused the variations in its pattern to appear, occurred! We will discuss that in due time. Steinhardt, then goes on to lay out 5 key takeaways, we learn from the CMB once the data is cleaned to achieve first approximation. I have highlighted each of them in bold, in the following quote. Thereafter, we will unpack his quote, and study the implications of these 5 salient features of the universe, in depth.
And the striking thing that one gets, if one reduces the resolution by just a little bit, is the first approximation, the universe is remarkably homogeneous. Remarkably uniform, in any direction we look and wherever we look. Furthermore we can use the data from this image, to infer what is the geometry of space. In principle, in general relativity, that geometry could be curved or warped. But in fact, what we discover, is flat - Euclidean. The laws of euclidean geometry hold beautifully, in this universe: the sums of angles in a triangle, add up to 180 degrees. Another interesting feature of this image is that it shows us that the matter and radiation were in thermal equilibrium, which means that they were at maximal entropy. But if you think about the total entropy in the universe, at that time, its actually much smaller than it could be. By many tens of orders of magnitude.... So there's something peculiar, about this low entropy as well. In fact, its partitioned in a strange way. Because the matter and radiation are in thermal equilibrium, which means they are at maximal entropy, whereas the geometry, the spacetime, the gravity, is nearly perfectly uniform: so almost no entropy. So how is it that we have a lot of entropy in matter/radiation, but almost no entropy in the gravitational degrees of freedom? And then finally, this phase, is well described by classical physics ... it can be understood from a classical point of view. Now, if you think about these five properties, and you think about the Big Bang, then you realize, the Big Bang is about as far away from these conditions as you can imagine" Paul Steinhardt
To restate them, the 5 "salient features of the universe," are: its homogeneity; its flat geometry; its extremely curious initial state of low entropy; its strangely partitioned entropy, between matter and radiation on one hand, and space-time, geometry or gravity on the other; lastly the fact that the early universe was classical and not quantum in nature. This 5 secrets found in the CMB, are wha Paul Davies was referring to when he said that: "The universe was set up - we don't know how - in a rather special state!" This "special state" turns out to be so special that it dictates, not only what followed, but what could follow! This special state, as we will quickly find out, lays out the physical limits of what could and could not follow it! We start on that exposition by deep-diving into each of the 5 salient features and unpacking them in detail. This is where all our earlier efforts in learning the basics, will pay dividends. If you did not take the time to wax-on/waf-off, you will not be able to follow the logic - simple though it is - that follows, as you will not have the necessary grounding in the basics of the physical laws that govern the universe. We start with a familiar word: homogeneity. Of course, whilst we have proved extensively that homogeneity and isotropy do not apply on any scale to the cosmos and the universe in our time; we are aware that the homogeneity found in the CMB is about how the universe looked before stars and galaxies appeared.
1. A Homogenous Early Universe
What homogeneity means in the context of the universe at initial conditions, which is the time-frame Steinhardt is discussing is that the universe looked the same in all directions because there was only one central object in existence. We will lay out the proofs for this in detail, shortly.
2. Spatially Flat Geometry
Let us now focus on geometry. Scientists confuse the general public when it comes to this topic, in no small measure, because they themselves are confused by the topic. The confusion arises due to scientists not having a strong grasp on what the geometry of the universe is a function of. Believers in the Big Bang, believe in inflationary theory, but their idea of what that is, is no more nuanced, than the often used example of an inflating balloon, with the galaxies being drawn on the 'surface' of said balloon. As the balloon is blown up, the surface becomes flatter and flatter. Of course this simpleton's example of how the universe expanded has no resemblance to reality. Nonetheless, incredibly, it was many professional scientists believe. The greatest error, people in society make is to relegate so-called scientific matters to experts, and then swallow scientific opinions down whole, without any critical thought as to their validity. If they did, they would discover, much to their surprise that most of what counts as serious scientific thought, barely scratches the surface of credible, never mind serious thought! Steinhardt gives his two cents:
Now, I'm imagining that many of you have read or heard about inflation before, and if I were to ask you, or if I were to ask a typical cosmologist in my field, 'how is it that inflation works?' Most of them, would describe it in a few words, using what I would call a classical physics view.... So how do we smooth the universe? Well, if we imagine space-time being analogous to a wrinkly rubber sheet, and we imagine inflation - which is a period of stretching very, very fast - you might think, as we stretch it, its going to appear smoother and smoother. Or, if I ask you how we flatten the universe with inflation? I think most you who have heard of inflation, and most cosmologists, would drum up pictures like this, which actually comes from a text, in which you imagine space-time being analogous to an inflating sphere! And, as you inflate that sphere - in fact the word 'inflation,' comes from that notion - as you inflate the sphere, the surface becomes flatter and flatter and flatter. And its the fact that people walk around with this very simple idea of how you smooth and flatten the universe that makes the idea of inflation, so compelling to people. It seems so simple. It seems so obvious. What could be simpler? Well the problems with the explanations that I just gave you is that, they're wrong! They're not just wrong, but they're misleading" Paul Steinhardt
A big problem with such analogies is that scientists have no idea what space-time is, whether it has a fabric, or how it works. Again, a priori speculation. What we are focused on right now, is what it means for the universe to be geometrically flat. Flatness in universal space terms, means how much material is in a fixed volume of Space. If there is too much mass in a set volume of Space, the material will it is argued, cause Space to shrink back on itself. We will be using Space with a capital 'S' to distinguish it from the normal usage of the word. On the other hand, if there is too little material within a set volume of Space, the universe will not be balanced gravitationally, and would thus keep growing in size, as Space kept on expanding outward. There are several ways these ideas are labeled and described, but we will not be worrying ourselves with them, for they are all wrong. What is relevant is to quickly explain what each scenario signifies, about the universe. When Space has too much mass in it, it is said to be "spherical" like a basketball. When it has too little mass, scientists describe it as hyperbolic, meaning saddle-shaped, like a horse's saddle. Again, the shapes and names are not important, for our universe is neither of those two shapes: our universe is FLAT! What does that mean? It means our universe contains just the right amount of matter and energy to maintain its overall shape, with everything in its place and a place for everything! Thus, there is a scenario where the universe is underdensity, one where it could have been overdensity, but as it turns out, the evidence tells us the universe is at Critical Density. This means taking together with the second salient feature of the CMB, there universe was spatially flat geometrically both at its beginning, and in our time! That is critically important to understanding the fate of the universe, because it means, the universe will never collapse in on itself, due to having to much matter and energy in too small a space. And it means, the universe will not expand forever, due to there not being enough matter to hold it at its current dimensions. Good news indeed.
How do cosmologists react to this fact? Not in happy way you might think. The Critical Density of the universe has been labeled the Flatness Problem, by the scientific community. In other words, for them, a stable universe that will be able to host life eternally is a problem. This problem goes all the way back to the start of the universe for scientists, because it means the initial conditions of the universe, its development, and its completion, all favour human life; something which for them seems to highly displeasing. I include a small excerpt from the 'Flatness Problem' page on Wikipedia:
The flatness problem (also known as the oldness problem) is a cosmological fine-tuning problem within the Big Bang model of the universe. Such problems arise from the observation that some of the initial conditions of the universe appear to be fine-tuned to very 'special' values, and that small deviations from these values would have extreme effects on the appearance of the universe at the current time. In the case of the flatness problem, the parameter which appears fine-tuned is the density of matter and energy in the universe. This value affects the curvature of space-time, with a very specific critical value being required for a flat universe. The current density of the universe is observed to be very close to this critical value. Since any departure of the total density from the critical value would increase rapidly over cosmic time, the early universe must have had a density even closer to the critical density, departing from it by one part in 1062 or less. This leads cosmologists to question how the initial density came to be so closely fine-tuned to this 'special' value" Flatness Problem Article - Wikipedia
Matt O'Dowd from PBS Space Time comments on how great a feat 1 part in 1062, over the size of the universe is:
Based on the precision of our measurements so far, we know that the curvature is within 0.4 of 1% of perfect flatness. Okay, so what? The universe is flat. No, actually, it's extremely weird. An expanding universe, doesn't tend to stay flat, even if its starts that way. Analogy: one way to bowl a strike is to keep the ball near the center of the alley all the way to the pins. If the ball isn't moving fast enough, then any deviation from dead center, will send it towards the gutter. Same with the universe. If the center of the alley represents a flat universe, then the gutters represent extreme curvature - in the positive or negative directions. If the universe starts out even a little bit not flat, then that not-flatness will amplify quickly. So, if our universe is flat to within 0.4 of a percent now, then in the first instant, the universe had to be flat to one part in 10 to the power of 62. That's like, rolling your ball really, really slowly and having it stay within 0.4 of a percent of the center of the alley, and the alley is a light year long. Nice bowling, universe" Matt O'Dowd - PBS Space Time (2:53 - 4:16)
From a person who is a great lover and believer in God, I want to emphasize that the measurements being within 0.4 of 1% is a human failure, a current limitation on our ability to measure accurately, and not a reflection of God's ability to be exacting. Nevertheless, the point is clear: the universe is at exact Critical Density! That presents a HUGE problem for cosmologists who believe in the Big Bang. Remember that earlier we discussed the tug of war between Fred Hoyle and his Steady State Theory, and Georges Lemaitre and his Big Bang Cosmology? What was the difference between those two camps - if you remember? What was the essential ingredient that made one theory opposed to the other? Critical Density! The steady state theory, claimed that the matter only came into existence as the universe expanded, while the Big Bang claimed the opposite: all matter came into existence at the Big Bang. Do you see the problem? No one argues that the universe is larger today, than in its early history. That being the case, how did an expanding volume of Space maintain Critical Density, if it always had the same amount of matter within it? You are starting to appreciate what I meant when I said the "rather special state," that the universe was in, initially, DEFINES what is, and is not possible!
But there is an even bigger problem for evolutionary cosmologists. I'll let Frank Wilczek, the recent 2022 recipient of the Templeton Prize - who already has a Nobel award in the bag - explain what cosmologists speculate took place in the Big Bang. Answering a question from Lawrence Kuhn about "let's take the moment of the Big Bang: in this incredibly energy filled, very high temperature extraordinarily dense thing. How could matter have formed from that event?"
Well, the matter was already there, in the sense that there was the energy, there were lots of quarks an anti-quarks, plenty of ingredients to make everything we see today - in fact, too much. So the right question is how does matter survive?" Frank Wilczek - Closer To Truth*(0:33 - 0:49)
The first thing we want to highlight, is that cosmologists believe that there was too much matter in the early universe. Some of the ideas of cosmologists are so far fetched, I will not detail them, as it would be a complete waste of time. It is futile to detail absurd ideas, only to later have to falsify them. What ideas I do present to you will be those that are either, at least skirting reality closely enough that they are worthy of mention, or because of having been well promoted by the scientific community over long periods of time, find themselves generally accepted as conventional wisdom, even if few know their details. This, of course, is the case with the Big Bang.
In the quoted clip, Wilczek goes onto describe that there was a billion times more mass at the beginning of the universe than we see today, and that this extra matter self annihilated. He proposes the existence of matter/anti-matter pairs, which cancel each other out. Then why is there something instead of nothing? There is a slight "asymmetry" in the matter, anti-matter ratios and what's left over from this asymmetry is the matter we have left over today. Following is his description of this supposed phenomena:
If we had the same number of quarks and anti-quarks, they would all have annihilated, to very high accuracy, and nothing would be left. So the reigning picture is that, in the early universe, you had quarks, say here's five quarks and [four] anti-quarks ... they annihilate and just one man is left standing, because he's the oddball. Now that was five against four. The reality is more like a billion and one, against a billion. This tiny asymmetry between quarks and anti-quarks, or if you like between matter and anti-matter is what survived from all that stuff to make the matter we see today" Frank Wilczek - Closer To Truth (0:50 - 1:38)
Hence there was a billion times more matter in the early universe than exists today, but all except a tiny fraction self annihilated, and everything we see in the cosmos today is a result of the small fraction of matter that survived this matter/anti-matter annihilation. Realize that the terms quarks and matter are used interchangeably. What is relevant for our discussion, is that all the matter that exists today, was present at the beginning of the universe. Lawrence Kuhn asks for clarification and Wilczek confirms that he has the correct understanding.
RLK: So, let me see if I have this right, at the beginning there was ... this incredibly dense, hot energy, and that from that, through Einstein's [e=mc2 formula] you had the formation of quarks and anti-quarks from this energy?
FW: Right. They're a form of the [energy]. One way in which the energy embodies itself, if you like.
RLK: But, there's an imbalance, a slight imbalance?
FW: A slight imbalance. Or, [it] may have been at the very earliest times there was accurate equality, that would be the most symmetric. But then there are processes, that are not quite symmetric, and so there comes to be a systematic little imbalance, that at first is hardly noticeable. You have a billion plus one of quarks, and a billion of anti-quarks, but then they almost all annihilate. Until, just this little guy, is left over, and that's, that's us. That's everything, that we think of as ordinary matter: stars; planets; galaxies.
You should immediately see gaps in the reasoning, or lack of it, as the case may be. Firstly, if what he was saying were true, then there would be a way to convert matter back into pure energy. No such conversion of physical matter into pure energy exists. When energy is released in nuclear bombs, it is the energy of the strong nuclear force, that was holding the subatomic particles together, that is released, not the energy that was originally used to create matter and anti-matter. If his theory was correct, this would be possible, at least in theory. It is not! Secondly, if matter came into existence through this super dense energy, what did the denseness, represent, if not matter? In other words, the Big Bang singularity is said to be super hot and incredibly dense, because, all the matter in the universe was fit into an incredibly small space. That is what the originator of the idea, Georges Lemaitre, called the Prime Atom. The conditions were hot and dense due to the presence of squashed matter. However, now we are being told it was the hot dense conditions of the energy that created matter and anti-matter. It's a catch 22, which is it? If there was no matter, what made the volume of Space hot and dense? You cannot speak of density of Space, without the presence of matter. More than that, the volume of Space becoming hot and dense is supposed to be a consequence of a constant volume of matter being fit into a smaller and smaller volume of Space. Here is Wilczek, again in his own words. Responding to a question from Lawrence Kuhn:
RLK: Frank, one of the great discoveries of the 20th century, is that the universe is expanding ... but if we take a step back, what does that imply? What can we learn from it?
FW: I think the most profound thing we learn, from the fact that the universe is expanding, is that it used to be much smaller. If you run the equations of physics backwards in time, which you can, the present expansion [will] be, of course a contraction. And, as the thing contracts, gravitational attraction means that it gathers steam. It gathers energy - imagine it running backwards. So the universe becomes much hotter, as well as denser, in the early times.
IN HIS OWN WORDS! How can that be? The theory which is supposed to underpin, no, define, the whole of mankind's understanding of the universe and reality itself, is so undercooked, that its purveyors have never thought about it deeply enough, to see an obvious and glaring self-contradiction? Electromagnetic materials are self repellent because we have electrons on our outer shells and the protons and neutrons are in the center. This is why we don't fall through our chairs, or the floor. Nick Lucid told us as much in his channel's Dark Matter episode:
... If it doesn't interact with light, it's not electromagnetic at all. That means we can't put it in a container either. Because, the reason that your hand doesn't go through things, is because of electric repulsion, right? ... That electromagnetism, is what slows things down and generates heat ..." Nick Lucid - Dark Matter Isn't Dark: It's Invisible (4:18 - 5:43)
So if you run the scenario backwards, all the matter being squashed into smaller and smaller volumes generates heat and overdensity. And if you start at the beginning, the a hot and super dense spacetime creates matter. Of course, none of it makes sense! If there was no matter, why was the spacetime hot and dense? How can an empty room be densely packed?
But, there is yet a still more glaring omission. Cosmologists, by their own assertion, claim Dark Matter constitutes more than 85% of all the matter in the universe. More than 5 times the amount of visible matter that exists, and yet it is quite obvious that their speculations, as to how matter was created, have no inkling of an invisible form of matter. It is shamefully apparent, that the hot dense energy, is not responsible, for the origin of the substance that forms the "scaffolding of the universe." What kind of model of the universe, has nothing to say about how 85% of what makes up reality, came to be? The hot dense soup of Big Bang cosmology is wrong on all counts then. It is wrong on how matter, came to be; it is wrong on how much matter was in existence at the point of the "rather special state" of the early universe that is represented by the appearance of the CMB; and it is wrong about the types of matter that existed - altogether missing the existence of Dark Matter, which we know could not have been created by baryonic means, since it is not an electromagnetic material.
Next, we deal with what exactly a homogenous universe, must have looked like? That, fortunately is the easiest part of our analysis. Homogeneity, we already know, means an environment looks the same from any location. How does that translate to the early universe? Homogeneity can only be represented in two ways under those conditions: firstly as the image in Illustration 14; secondly, as the image in Illustration 15. We know that no part of the universe resembles the second of our illustrations, hence the only configuration that was possible to satisfy the condition of homogeneity is Illustration 14! Moreover, since the earth is at the center of the CMB, and the the evidence tells us that the galaxies are flying apart, around that central position, we know that whatever celestial body represented the matter that formed the Critical Density, at this initial stage was in our Solar system, and that it was not a star, since stars did not yet exist, by all accounts. That is not under dispute. Hence, the mass at the center of of the volume of Space was a planet, we will not speculate about which planet. We will allow the evidence to narrow that down for us as we proceed. We will now move on, to why and how the early universe came to have low entropy.
One central object fits the scenario for homogeneity. For, in which ever direction you, look into the rest of the universe, you will see only nothingness. This agrees with our gravitational evidence. Below is the second - and only other way - homogeneity can be manifested.
I have put in the bare number of planets or heavenly bodies - just enough to establish what a multi object homogeneous arrangement would look like. All the additional objects (after the first one), would have to be equally spaced and mirror each other's positions in Space. The universe looks nothing like that - as we have seen on our section dealing with Subir Sakar's excellent work. (Which still has not been addressed by the scientific community.)
3. Low Entropy: The Meaning Behind Thermal Equilibrium
Recall, how Jim Peebles characterized the initial conditions of the universe: ""
I would say an iconic piece that shows tangibly, that the universe, had to have evolved from a different state. Because, this [the CMB spectrum] is a thermal spectrum. Our universe, as it is now, is transparent to this radiation. There's no way it could force the radiation to relax to this thermal equilibrium. The universe had to have evolved from a state in which it was dense and hot enough to have relaxed to equilibrium and then expanded away from it" Jim Peebles (24:50 - 25:26)
Alternatively, we have Paul Davies, a winner of the famed Templeton Prize, stating a similar point,
When you think about the early universe, you think about the cosmic background heat radiation. And that radiation turns out to be very very close, to what we call thermodynamic equilibrium" Paul Davies
So, Peebles calls it a thermal spectrum, and Davies refers to it as heat radiation. They are both wrong! How do know? We now know that there was no hot dense primordial soup, because the matter in the "special state" was at critical density with the volume of Space that existed back then. Critical density exists in a binary reality with the proposed dense, hot plasma of Big Bang cosmology: you either have one or the other. To have a dense hot plasma, means all the matter, we currently see, existed in a volume of Space, smaller than the head of pin, by many many times, hence it means there was no Critical Density, the farthest thing from it. On the other hand, if there was Critical Density, it automatically, means there could be no dense, hot soup. As soon as you have Critical Density, there is no possibility of over density - by definition! If there is no over-density, there are no superhot conditions, because baryonic matter is not forced into a smaller volume of Space than is defined by Critical Density. Thus, we see that the relationship between Critical Density, and the Big Bang Singularity, is a binary one: you either have one or the other, but you cannot have both!
The initial critical density as reflected in the CMB, represents a different amount of matter and a different volume of Space, than exist today. However, it is the same critical density that the universe evinces as a whole, possesses down to our day, and we don't live in an extremely hot and dense singularity. We know that, for reasons we have already explained. These facts are conspiring to tell us something significant about the early universe. Paul Steinhardt explains the low entropy, in this way: "Another interesting feature of this [CMB] image, is that it shows us that the matter and radiation, were in thermal equilibrium." What does that mean? Put simply, it tells us that matter and radiation were at the same temperature. 'Thermal equilibrium,' is shorthand for saying two entities are at the same temperature. However, though this is almost always as a result of coming to thermal equilibrium through interactions, it doesn't have to be so: and in the case of the "rather special state" of the CMB, it is not. How do we know?
How do we know that this thermal equilibrium, could not have been a result of normal thermal processes? As we have studied previously, thermal radiation is a degree of freedom. It is one way that an element can dissipate heat away from itself, and out, into its surroundings. So when an electron gives off thermal radiation, it drops down the energy ladder, by the same amount of energy, it has just released into the environment. What's more, we have already learnt that such processes are always aimed at the outside environment and never occur internally. That means, if the CMB was a result of matter expelling heat, it could not be at the same temperature as the matter that expelled it. Hence, the CMB radiation could not have been a form of thermal radiation! Secondly, if the CMB radiation was not outgoing from a source of matter, the only way it could be in contact, with matter is if it was incoming radiation. The common temperature with matter was thus measured upon contact, and was not the result of repeated interactions, leading to thermal equilibrium, as is normally the case. This interesting fact, we know from the 3rd and 0th laws of Thermodynamics. As we refresh our minds on those fundamental laws of nature, we recall what Eddington said:
If someone points out to you that your pet theory of the universe is in disagreement with Maxwell's equations - then so much the worse for Maxwell's equations. If it is found to be contradicted by observation - well, these experimentalists do bungle things sometimes. But if your theory is found to be against the second law of thermodynamics I can give you no hope; there is nothing for it but to collapse in deepest humiliation" Sir Arthur Eddington
That's how important, the laws of Thermodynamics are! The third law states that: "If two systems are both in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with each other." Of course, the third system is the temperature itself. Since, the temperature of the matter is the same as the temperature of he 'incoming' radiation or light, as the CMB testifies to, it is obvious that this determination of shared temperature occurs upon impact! That is, it is not, the result of repeated collisions, as is the case of two different substances or elements coming to thermal equilibrium. That phrase is correct, only in that it describes a state of two different entities sharing a common temperature, but it is wholly misleading, when applied to how, such entities came to share the same temperature. The empirical evidence from the CMB is that matter and light had the same temperature upon contact with each other. They were not at two different temperatures, and then settled to a common temperature through interaction. A good question to ask, is if the radiation, let's use the synonymous word 'light,' did not emanate from matter, and there were no stars, where did it originate from? We will answer that question a little later, once we have more facts at hand. For now, we hold onto the main point, the CMB could not be thermal radiation from matter, because that would immediately mean, the two entities could not be at the same temperature. Carnot's engine taught us that. The surroundings would have to be a heat sink, in other words cooler than what is expelling the heat, for the heat to transfer, otherwise, there is no movement of heat. A common temperature between two entities means there is no heat transfer between them! The conclusion is inescapable: if the temperature between matter and light was the same, then the light could not have been produced by the matter. The light was not a form of thermal radiation, or heat radiation, as Paul Davies, put it.
But, as you think deeper on this subject, you will realize an even more disturbing fact. Since thermal equilibrium means no work can be done, and the universe was at Critical Density, this scene means no work was being done: but more than that, it meant no physical baryonic WORK, could be done! That is the most jarring significance of the "rather special state" that Paul Davies spoke about. Since no work could be done, according to the laws of thermodynamics, it means the universe could not expand, and no natural process could take place: not gravitational collapse, nor any other process. Nothing could move! That's what the laws of thermodynamics tell us. That being the case, the real question is what broke the stalemate? For, it is quite apparent that the universe did go onto develop, from that early state, into what we see today. Interestingly, the lesson from thermodynamics, is that whatever, was responsible for breaking the deadlock, could not have been a baryonic process, for the laws of thermodynamics hold complete sway over all baryonic processes! Let me repeat that for clarity and emphasis: whatever caused the baryonic stalemate, to be broken, could not have been a baryonic process! In other words, no form of evolutionary process could be responsible for developing the universe from its initial state, to the one we see and experience, today: NO BARYONIC PROCESS: not cosmic evolution; not gravitational collapse - NOTHING!
Why Not Cosmic Evolution!
We now come to the crux of the matter regarding the failure of all current scientific theories, and how scientists came to be so misguided. The first thing we have to address is, what understanding does the evidence, actually support? And, what are extrapolated speculations, that are in no way justified by the evidence?
Helping us in deciphering the perplexing problem is, once again, Sabine Hossenfelder. In a late 2019 video entitled: "How Did the Universe Begin?" she goes through all classes of current theories on the subject and shows which are scientific and which are not - and why. I will tell you that none of the current crop of so-called scientific theories met the minimum threshold to be considered in-line with the scientific method - and that included many people's most cherished theory: the standard model of the universe, the Big Bang theory. As usual, we will quote the relevant portions, and then unpack them to clarify their meaning and significance:
Today, I want to talk about the beginning of everything, the whole universe. What do scientists think [about] how it all started? We know that the universe expands, and as the universe expands, matter and energy in it dilutes. So, when the universe was younger, matter and energy was much denser. Because, it was denser, it had a higher temperature. And a higher temperature, means, that on the average, particles collided at higher energies. Now you can ask: 'what do we know about particles colliding at high energies?' Well, the highest collision energies between particles that we have experimentally tested, are those produced at the Large Hadron Collider. These are energies [at] about, a Terra-electron Volt or TeV for short, which if you convert it into a temperature, comes out to be 1016 Kelvin. In words: that's ten million billion Kelvin ... So, upto a temperature of about a TeV, we understand the physics of the early universe, and we can reliably tell what happened. Before that, we have only speculation. The simplest way to speculate about the early universe, is just to extrapolate the known theories back to even higher temperatures, assuming that the theories do not change. What happens then, is that you eventually reach energy densities, so high, that the quantum fluctuations of Space and time become relevant. To calculate what happens then, we would need a theory of quantum gravity, which we do not have. So, in brief, the scientific answer is: that, we have no idea how the universe began! But, that's a boring answer, and one you cannot publish! So, it's not how the currently, most popular theories for the beginning of the universe work" Sabine Hossenfelder (0:00 - 1:59)
Startling admissions, from a leading theoretical physicist of the best kind - the honest kind. Before unpacking her words, we will underscore them, by adding technical weight to her admission. The one thing lacking in her statement, was exacting numerical values quantifying the size of the gap, between the highest temperatures achieved in the laboratory, and the erroneous and unjustified extrapolation of observational evidence, to a time in the history of the universe, when mankind could not possibly have any knowledge, of what took place. We will add weight to Hossenfelder's assertions by also quoting Steinhardt, on the same topic. However, they both commit an error, which we cannot overlook: for accepting it, means we are accepting misdirection.
This jarring reality, is a detail hidden inside the nature of this gap: for the temperatures that have been achieved experimentally in laboratories, have nothing to do, with what has been observed! This is a terrible sleight of mind, that whether done intentionally, or not, has the effect of conflating two ideas that have no correlation to each other. This conflating of two independent realities is committed by both Hossenfelder and Steinhardt. He thus gives further credence to a demonstrably false notion, which we will now give attention to - and whose falsehood we will demonstrate. Thereafter we will quote and discuss his quote in full, reviewing it in tandem with Hossenfelder's original quote, for the purpose of verifying the valid portions of their quotes. But, before we can focus on the valid portions, we have to root out the aforementioned error. Both Hossenfelder and Steinhardt, claim that there is evidence for a hotter, denser universe in the far distant past. This is clearly not true. There is neither any observable data, nor any empirical evidence for this assertion. This is the danger of extrapolating! Their error - whether intentional, or not - is that they conflate the observational evidence, with the theory that extrapolates it and tries to make it backwards compatible with the early universe. There is no justification for this. The observational evidence, is not retroactive: it cannot be applied to earlier supposed conditions, which are an extrapolation of an unfounded theory - and for which there is no evidence!
The Observational Evidence: Red-shifted Galaxies
There is universally acknowledged proof that the earth, our solar system, and indeed the Milky Way galaxy, are all sitting at the center of a cosmic play, where all the other galaxies are moving away from us, in all directions, and the farther away they are, the faster they are moving away from us. This is not controversial! This discovery, was what Hubble quantified almost a century ago. It proved to be the key detail, that would allow him to realize that the universe had undergone expansion in its history, it was not static, as had up to that time, always been conventional wisdom. All cosmologists freely admit as much, and both Hossenfelder and Steinhardt, make the same assertion, that there is evidence for the expansion of the universe. With this, all who are acquainted with the evidence must agree. This much is true, and easily provable from empirical data. Wendy Freedman expresses the matter thus,
A uniform expansion, the further away a galaxy is, the faster it's moving .... We have now measured, so-called redshift for these galaxies, for literally, a million or so objects and they're all red-shifting, they're all participating in this outward expansion of the universe. So, the implications of it, Hubble measured an empirical relationship: it just tells you that the further away a galaxy is, the faster it's moving. The implication of that result, if you put it in the context of Einstein's general theory of relativity, is that the universe is expanding" Wendy Freedman - Closer to Truth: Why is the Universe Expanding? (7:16 - 8:12)
With that part of Hossenfelder's and Steinhardt's forthcoming statement, there is no problem. The error arises in what they next say. Since, we have thus far, only quoted Hossenfelder, I will relate the error to her words, but you will be able to spot it once we cover Steinhardt's testimonial, on the subject.
We know that the universe expands, and as the universe expands, matter and energy in it dilutes. So, when the universe was younger, matter and energy was much denser. Because, it was denser, it had a higher temperature. And a higher temperature, means, that on the average, particles collided at higher energies. Now you can ask: 'what do we know about particles colliding at high energies?' Well, the highest collision energies between particles that we have experimentally tested, are those produced at the Large Hadron Collider. These are energies [at] about, a Terra-electron Volt or TeV for short, which if you convert it into a temperature, comes out to be 1016 Kelvin. In words: that's ten million billion Kelvin ... So, upto a temperature of about a TeV, we understand the physics of the early universe, and we can reliably tell what happened" Sabine Hossenfelder
Nothing in this portion of Hossenfelder's quote has any foundation in reality. Matter and energy does not dilute, as the universe expands. If it did, then the universe could not maintain Critical Density, which as we have already discussed, we know it does maintain. Critical Density, is one of the pillars of the universe, like matter and Space itself! It is a factor that cannot be factored out! At all times and through all stages of its development, the universe was in Critical Density. We know that the "rather special state," the universe was in, initially was at Critical Density, as borne out in the CMB data, and we know that it is at Critical Density now. As for in between, we can determine critical density, because, by looking at different scales of the universe, we are looking at different stages of its development, and at each scale that scientists look at the universe at, they always see Critical Density. And since, the different scales, relate to different times or epochs in the history of the universe, we know that the universe was, and has always been at Critical Density. This fact alone, means matter does not dilute as the universe expands!
That being the case, Sabine's following reasoning: "So, when the universe was younger, matter and energy was much denser," is not valid. Since we have falsified the notion that matter dilutes with the expansion of the universe, we understand clearly, that the reverse - which is what Hossenfelder has assumed - must also not be true: if we run the expansion of the universe back, to a time when it was younger, according to the principle of Critical Density: matter and energy would not have been "much denser." Instead, matter and energy, would have been, the same as they always were: at Critical Density! The truth behind the reality of Critical Density, is that, it means more and more matter came into existence, as the universe expanded, as the volume of Space was increasing!
Does Critical Density Ever Allow for Increases in Temperature & Density?
A big part of understanding how things work, is to fully appreciate the consequences of their dynamics! What does that mean, when it comes to Critical Density? What are the full range of implications behind this fundamental pillar of the nature of the universe?
Critical Density, means there is always the right amount of matter and energy, to fill a certain volume of Space. Since, the universe has always been at Critical Density, it means, there has never been a time, when the universe was denser or hotter than it is now! Of course, we are not naive. This does not mean we think there were no objects like the Sun, of course there were many star like objects in the history of the universe. As there many today. But that is not what people who espouse a hotter denser universe mean, when they invoke such a hotter and denser scenario. No, they mean something fundamentally different, which alters the fundamental laws of our universe. It is that speculative environment that Critical Density falsifies. If Critical Density is a constant through all stages of universal development, then the conditions we witness today, are similar - in terms of Critical Density and the conditions it allows - to what has existed throughout the full history of the universe: from the time the CMB first appeared, up until the present day! Thus Sabine's assertion that the because the universe "was denser, it had a higher temperature," is false. That inturn undoes the next parts of her argument: "... a higher temperature, means, that on the average, particles collided at higher energies"
And a higher temperature, means, that on the average, particles collided at higher energies. Now you can ask: 'what do we know about particles colliding at high energies?' Well, the highest collision energies between particles that we have experimentally tested, are those produced at the Large Hadron Collider. These are energies [at] about, a Terra-electron Volt or TeV for short, which if you convert it into a temperature, comes out to be 1016 Kelvin. In words: that's ten million billion Kelvin ... So, upto a temperature of about a TeV, we understand the physics of the early universe, and we can reliably tell what happened" Sabine Hossenfelder
It is these secondary assertions that are an unfounded extrapolation and hence, a divergence, from the agreed upon observational evidence of galactic redshifts. Scientists estimate the Sun to be 15 million degrees Celsius. At such temperatures the difference between Celsius and Kelvin (273) is negligible, so I use the temperature scales interchangeably. Recall, that Sabine said the highest temperature attained at the Large Hadron Collider was 10 million billion Kelvin. That means the temperatures reached experimentally on earth are roughly 3 orders of magnitude higher than the estimated temperatures at the center of the Sun. She then claims that: "So, upto a temperature of about a TeV, we understand the physics of the early universe, and we can reliably tell what happened." This statement is clearly incorrect! This is where both Hossenfelder and Steinhardt commit their gross error of reasoning. Her premise is wrong! That much we know, because she, and Steinhardt alike, factor out Critical Density, and pretend a smaller universe means a "a denser and hotter" universe, when nothing could be further from the truth. Continual Critical Density - from the CMB to the present - makes sure of that!
Two things are true: humans have observed galactic redshift, which means the universe is now bigger, than it was in its past - the universe has expanded; a second truth is that in our experiments, humans have achieved incredible temperatures, almost 1 000 higher than the estimated temperature at the center of the Sun. However, these two facts have nothing to do with each other. The link that scientists try to use to relate them to one another: a smaller universe being equivalent to a denser and hotter universe is proven false by one of the pillars of the universe - Critical Density! As such how atoms act under those extreme laboratory conditions, has absolutlely nothing to do, with the history of universe, or understanding it! Conflating these two independent truths into a jumbled picture of the history of the universe is not Science - or scientific!
Extrapolating the Evidence is Sleight of Mind!
If we are to run the development of the universe backward, we have to do so according to the known laws and principles that have guided its forward development. And we know that one of those foundational principles is Critical Density. Thus anytime scientists, or anyone else tries to reverse the arrow of the development of the universe, they have to do so according to those principles. For this reason, Critical Density always has to be factored in to the functionality of the universe, no matte what epoch of its history we are considering. Doing so without the aid of Critical Density is not extrapolating, but sleight of mind. Sleight of mind, is just like sleight of hand, however, instead of using quick hands to furnish the trick, 'sleight of mind,' using suspect reasoning to reach conclusions that are not justified by the evidence. Whether Hossenfelder and Steinhardt fell into this trap willingly, or they were misled, and are just repeating something they were taught and accepted uncritically, we don't know - or care: the point is that, we will not accept any claims naively!
Now, that we have rooted out the false reasoning, you will be able to easily spot it in Steinhardt's quote, which we will now consider. Recall, that the point of quoting Steinhardt was to add support to Hossenfelder's statement that there is compelling evidence for the expansion of the universe.
So, the question we want to ask today, is whether it's time to take the Big Bang out of the Big Bang theory? That might seem like a radical idea at first, but it's not as radical as it seems. It's true that there's an abundant amount of empirical evidence for the Big Bang theory - any cosmologist would tell you that. At the same time, there's not a shred of empirical evidence for the Big Bang. Why is that possible? Well, it's because the Big Bang theory is really a merging of two very different ideas. Ideas that are on very different scientific footing! Idea 1, is that the observable universe was once smaller, hotter, denser: and has been expanding and cooling for the last 13.8 billion years. We have a lot of evidence for that, beginning with Edwin Hubble's observations from the 1920s, all the way up to the most recent observations from the most sophisticated telescopes and detectors, on the ground, in space and balloons. And with that evidence, we can trace the evolution of the universe from the present, going back in time to when the first atoms formed, about 400 000 years after the beginning of expansion. And even further back, to when, the universe had a temperature that was at nuclear fusion temperatures: and protons and neutrons could be fused together to form the first heavy nuclei, in the history of the universe! We can go beyond that using experiments in the laboratory from particle physicists, which take us a few orders of magnitude earlier in time - indirectly. But, idea 2, is the idea that the universe began in a Big Bang! And, to get to the Big Bang, we have to extrapolate 15 orders of magnitude higher in temperature, than anything we've observed in a laboratory; or 60 orders of magnitude higher in density. And that's why, we have no evidence for the Big Bang, itself!" Paul Steinhardt (0:16 - 2:37)
It is curious that Steinhardt, in trying to correct the error of the Big Bang says: "Why is that possible? Well, it's because the Big Bang theory is really a merging of two very different ideas. Ideas that are on very different scientific footing!" But he, himself, then proceeds to merge two "very different ideas. Ideas that are on very different scientific footing!" Why does he see through the ruse in one case, and not in the other? Nevertheless, the purpose of us quoting him was to show the gap between the temperatures that have been achieved experimentally, in research facilities, and the thresholds that are proposed by the Big Bang theory. 15 orders of magnitude higher in temperature, is equal to adding 15 more zeros to the highest temperature yet achieved on earth - 15 more zeros. Nevermind, the fact that we already understand that those laboratory temperatures also have nothing to do with the history of the universe, as we have just proven in detail. Hossenfelder, then continued with her evaluation of the current state of Science. Her next point was that, even if scientists think they understand what happens at the highest temperatures reached on earth, the jump from those temperatures to the proposed temperatures in the Big Bang, is so vast that outside of those results: "we have only speculation." Why? Because for scientists to try and bridge the gap between unrelated experiment, and the speculated conditions of the Big Bang, calls for a bridge they do not have. As such, all their speculations are not scientific! To remind you, her is another sample of her quote,
The simplest way to speculate about the early universe is just to extrapolate the known theories back to even higher temperatures, assuming that the theories do not change. What happens then, is that you eventually reach energy densities so high that the quantum fluctuations of Space and time become relevant. To calculate what happens then, we would need a theory of quantum gravity, which we do not have. So, in brief, the scientific answer is that we have no idea how the universe began" Sabine Hossenfelder
Let's take her statement in reverse - from end to beginning. Once scientists reach a certain operating temperature, that temperature effects the nature of the substances that make up the universe, changing them from a classical predictable nature, to an unpredictable, quantum nature. These high temperatures would affect not only how matter acts, but also time and Space itself! To be able to predict what would happen under such circumstances, scientists need a theory of Quantum Gravity, which they do not possess, hence, they cannot bridge the knowledge deficit they have about how the extremely hot, dense, early universe behaved.
Our job is to never accept any assertion - naively, remember! To that end, we start by defining Quantum Gravity. This is the natural end state of the false concept of extrapolating the expansion of the universe backwards, until all Space and matter fit into a single infinitely dense and hot singularity (point). What do you instantly recognize as wrong in that scenario? WE KNOW THAT SPACE AND MATTER ARE ALWAYS AT CRITICAL DENSITY. That means, we know that there is no such thing as Quantum Gravity, there is no time in the history of the universe, where there was an over-density of matter, and too little Space for it to fit in - that would be the opposite of Critical Density. WE KNOW THAT! We understand why scientists will never discover a theory of quantum gravity, because: Quantum Gravity and Critical Density, are binary realities, you can only have one, or the other - never both at the same time. And, since Critical Density, has been continual throughout the development of the universe, that leaves no room for when "quantum gravity," could have held sway.
Another alarming misunderstanding about the nature of the universe found in this worldview, is that Einstein's unified 4-dimensional structure that incorporates Space and Time, which is universally known as Space-time, is thought of as being a baryonic entity! This profound miscalculation, highlights why so much of current cosmology is dangerously divergent from true Science. Think for yourself: try and come up with at least three reasons why Space could never be a baryonic entity. We know that according to the Big Bang theory, it must be baryonic, because it is susceptible to heat and density! Only electromagnetic entities, are susceptible to heat and density for the same reasons we learned about from Nick Lucid. The structure of atoms, has protons and neutrons in the middle and electrons outside, orbiting the nucleus. This is what is responsible for you not falling through your chair, or the ground: electric repulsion between the electrons in your chair and you are pushing against each other - and keeping you in your place! Heat is the result electrons exchanging kinetic energy with each other through collisions, as we learned about earlier, in our section on Carnot and Clausius. The Big Bang theory then posits that if all the mass in the universe were to be fit into smaller and smaller volumes of Space, then eventually there would be so many collisions that the heat would reach infinity. Now, they assert that this would, in turn, make Space, itself fluctuate. For that to happen Space would, similarly have to be electromagnetic in nature. Of course Space is nothing of the sort. Here are the three reasons: 1) Space can travel faster than the speed of light! There are galaxies that are said to be superluminal (traveling faster than the speed of light). Hubble discovered an empirical relationship: "... it just tells you that the further away a galaxy is, the faster it's moving," said Wendy Freedman. Hence, since Hubble's groundbreaking work, the farther scientists have looked back in time, due to improved technologies, i.e., the greater the distances they are increasingly, able to peer into, the faster the velocity of the galaxies that they see: some have been claimed to be moving faster than the speed of light. How is that possible, since nothing can move faster than light! It is because, it is not the galaxies, that are moving at those velocities, but rather, it is the region of Space, in which the galaxies are embedded, that is moving faster than the speed of light, because Space - unlike, visible baryonic matter can move and bend faster than the speed of light. Our favourite theoretical physicist explains:
Einstein's theory of general relativity says you cannot accelerate objects from below to above the speed of light because that would take an infinite amount of energy. However, this restriction applies to objects in Space-time, not to Space-time itself. Space-time, can bend, expand, or warp at any speed. Indeed, physicists think that the universe expanded faster than the speed of light in its very early phase. General Relativity, does not forbid this" Sabine Hossenfelder - Warp Drive News: Seriously (1:08 - 1:39)
The point is clear: any entity which can travel faster, than the speed of light cannot - by definition - be electromagnetic in nature. This leads us to reasons, two and three: 2) Entities that are not electromagnetic in nature are not susceptible to densification, which is a function of the compactness of electrons within, a set volume of Space; and 3) due to reasons one and two, Space can also, logically not be susceptible to heat, as heat is also a function of the transfer of kinetic energy through motion (collisions). Now, some might object and say, but the infinite heat and density are properties of the baryonic matter - not Space. That is true, according to the theory, but their effect is transferred to the fabric of Space-time through quantum fluctuations, which means the Space-time is susceptible to the same dynamics. It is obvious that for Space-time to have quantum fluctuations, it would have to be made of electromagnetic particles, i.e., baryons! However, as we have just learned, Whatever Space actually is, it cannot possess such properties: its functionality forbids such dynamics! That much is not in doubt, since we observe that Space has indeed moved millions of galaxies away from the earth, in all directions. Hence, since the functionality has been established, it is the current definition of Space, as a baryonic entity, that is incorrect! All empirical evidence and observational data, tell us that Space, whatever it is, is not baryonic! If only there was a substance known to man, that was not electromagnetic, it would have the perfect EVIDENCE PROFILE, to fulfill all the functions of - Space! We press on.
We end our analysis of Sabine's "simplest way to speculate" quote by giving attention to its initial phrase: "The simplest way to speculate about the early universe is just to extrapolate the known theories back to even higher temperatures, assuming that the theories do not change." We now know that scientists do not have the experimental ability to extrapolate their theories back in time. Moreover, we know, that even if they had such capabilities, they would have no effect on scientific knowledge about the early universe, because the concept of extrapolating the forward expansion of the universe backwards, is itself, an error in judgement and logic. Hence, their theories, would generate false conclusions, as they indeed do, because the foundational concept underpinning their theoretical framework, in incorrect! Any exercise, of mentally reversing the development of the universe so that it gets smaller and smaller, must proceed within the parameter of continual Critical Density, since, from the moment light first appeared in the form of the CMB, there has never been a period in the development of the universe, when it was not at Critical Density! So Hossenfelder's "simplest way to speculate about the early universe," is itself a theoretical failure and a non-starter on logical grounds - quite apart from its technical impossibilities as highlighted by Hossenfelder and Steinhardt.
Sabine Hossenfelder's Conclusion About the Quality of All Current Cosmological Theories
So, in brief, the scientific answer is that we have no idea how the universe began. But that's a boring answer and one you cannot publish, so it's not how the currently most popular theories for the beginning of the universe work. The currently most popular theories assume that the electromagnetic interaction, must have been unified with the strong and the weak nuclear force at high energies. They also assume that an additional field exists, which is the so-called Inflaton Field. The purpose of the Inflaton, is to cause the universe to expand very rapidly early on, in a period which is called 'Inflation.' The Inflaton Field, then has to create all the other matter in the universe and basically, disappear, because we do not see it today. In these theories, our universe was born from a quantum fluctuation of the Inflaton Field: and this birth event is called 'the Big Bang!' Actually, if you believe this idea, the quantum fluctuations still go on outside of our universe, so there are constantly other universes being created. How scientific is this idea? Well, we have zero evidence that the forces were ever unified and have equally good evidence, namely none, that the Inflaton Field exists" Sabine Hossenfelder - Warp Drive News: Seriously (1:43 - 3:07)
Under the umbrella of theories that comport to the scientific method, she lists NONE. She then points out a sad motivation: the fact that scientists have to eat, "But, that's a boring answer, and one you cannot publish." Since cosmologists earn their living by expounding theories and then explaining them to eager audiences - think of the likes of Niel DeGrasse Tyson, Brian Cox and Brian Greene among many others - she points out that saying I have no idea how the universe began is not a plausible way to earn a living. For that reason, she further states that: "... so it's not how the currently most popular theories for the beginning of the universe work." In other words, if we were to make two separate lists under the headings: "We have an idea about how the universe began," and a second list that was headed: "we have no idea how the universe began," all current so-called scientific theories would fall under the second list! That shouldn't amaze you. Whereas, many view science as unending quest for truth, we now have evidence that scientists also have bottom lines, and they must earn a living, hence many facing a knowledge barrier, just create empty speculations and pass them of as theory. It pays. The cash prize for a Nobel prize is in the millions, and the Templeton Prize is even more lucrative.
So we know promising ideas about the origins of the universe is: "... not how the currently most popular theories ... work," Hossenfelder, now points out that in the absence of any valid ideas, the current crop of theories, are instead, based on ... "assumptions!" These assumptions include that all the forces were unified, in the early universe. And, that there was an imaginary field called the Inflaton Field, which magically caused the universe to "expand very rapidly early on" in a period called "Inflation." While, it was rapidly inflating the universe, the Inflaton field also created all the matter in the universe, and then DISAPPEARED. Yes, that's the actual claim, of the people who created Inflation theory. I think you can see why one of the three fathers of Inflation Theory, Professor Steinhardt is now so strongly against it! As fantastical as this sounds, Sabine's summary is factual. Alan Guth, the first of the three collaborators who created Inflationary theory is sticking to his guns, and in a recent interview with Robert Lawrence Kuhn, stated almost word for word, everything that Sabine credits to the creators of Inflationary theory. What follows is the conversation he had with Kuhn, describing his "currently most popular" theory of Inflation. It's amazing what an imaginative mind can make out of "we have no idea how the universe began:"
AG: Inflation, is based on ideas coming out of particle physics, which tell us that our theories predict that at very high energies, there should actually exist forms of matter, which turn gravity on its head, and cause gravity to behave repulsively, instead of attractively. And the inflationary theory, is basically the hypothesis that this repulsive gravity, was the bang of the Big Bang. It's what set the universe, into this period of gigantic expansion. The gravitational repulsion leads to an exponential expansion, which means that there's a certain time in which the universe doubles, and if you wait the same amount of time, it doubles again, and then doubles again .... To get the universe from the size that we think it had at the beginning of inflation to what it needs to have had, at the end of inflation, to ultimately include everything that we see, requires about a hundred doublings. These doublings happen unbelievably quickly, using the physics of what particle physicists call Grand Unified Theories. Then, the doubling time was about 10 to the minus 37 seconds [10-37]: decimal point, 36 zeros, one at the very end. Unbelievably short amount of time.
RLK: So, if a hundred of these it takes 10 to the minus 35 [10-35] seconds?
AG: That's absolutely right ... that's still an unbelievably short amount of time!
RLK: So, in this period of time, the whole universe as we known it, was created?
AG: Essentially, that's right. Uh, inflation is not a theory of the ultimate creation of the universe. In that, to start inflation, one needs a bit of matter: approximately a gram, it turns out. But, once you have this gram, inflation actually does describe how all the rest of the matter that we see, which of course, is vastly more than a gram, is created. Absolutely!
RLK: Now, it sounds like we're getting something for nothing, because how can you have energy being created, when we know there's a very tight law of conservation of energy and matter?
AG: It [long pause] does sound amazing, and I sometimes refer to the Inflationary creation of the universe as the ultimate free lunch! So, we have this exponential expansion, and it ends because this repulsive gravity material is unstable, so it starts to decay, into normal forms of matter, and releases energy in the process. And its that release of energy, uh that becomes the energy of the universe that gets produced. The shocking thing is that even though, the total energy is always conserved, one has an instinct to believe that energies are always positive; so that to have a lot of energy in some place, you need to have started out with a lot of energy someplace! That's what falls by the wayside. Inflation takes advantage of the fact - which has really been part of physics for a long time - uh, that not all energies are positive. And, in particular, the gravitational field has a negative contribution to the total energy of whatever system it's part of. So, as inflation goes on, more and more positive energy goes into the creation of matter of various kinds. But, at the same time, more and more negative energy is created in the form of this gravitational field, that just fills the ever-expanding region of Space - and they balance! So, the total energy remains what it was when you started, which was very, very close to zero! And, shockingly, it it really is consistent. When we look at our observed universe, uh that the total energy and stars and galaxies, and vast amounts of matter that we see, uh, throughout the universe, is cancelled, by the negative contribution of the gravitational field that fills the universe! So the total energy of our universe is consistent with being ZERO!
RLK: Now, all of this matter, then, is created at the end of inflation?
AG: That's right. It's created with the form of this repulsive gravity material, as inflation goes on, but becomes normal matter at the end of inflation.
That was a long conversation, but as I said earlier, we will document in full what the claims of cosmologists are. At this point, I want to stress that Alan Guth is an adult. According to his Wikipedia profile he was born on 27 February 1947, which at the time of this writing makes him 75 years old! From the outset, we understood that his theory falls under the of list of theories who refuse to admit that: "we have no idea how the universe began." In her analysis, Hossenfelder, went onto to ask, and answer the question: "How scientific is this idea?" - about the Inflationary universe. Her answer was unequivocal:
Well, we have zero evidence that the forces were ever unified and have equally good evidence, namely none, that the Inflaton Field exists" Sabine Hossenfelder
Simply put: the theory is not scientific, since it has zero evidence backing it up, and for all the reasons we have already covered. Alan Guth's Wikipedia page concluded his bio with this paragraph:
By 1983, Guth had published a paper describing how his supercooled universe scenario was not ideal, as the "triggering mechanism" to exit such a state would require "extreme fine tuning of parameters" and felt a more natural solution was required. However, this did not deter him from the belief that the universe expanded exponentially in a vacuum in its early lifetime" Alan Guth Article - Wikipedia
In other words, he himself does not believe, what he is peddling, but as it's the best he has come up with, so he will boldly double down. In her continuing assessment, Hossenfelder, then proceeds to give alternate theories, but the details are no longer important, because we understand that, these theories too, fall under the same umbrella of people who refuse to admit that they "have no idea, how the universe began." What should be troubling you is something that is much nearer to home: the fact that you have also bought into these unhinged speculations, hook line and sinker! Do you not believe in multiple universes? That's where such beliefs originate. Do you not believe that there are alternate versions of yourself in parallel universes, that represent every possible outcome that your life could take? That there is a poor version of you, and a rich version of you and everything in between, living their lives out concurrently with you? Such beliefs originate in inflationary theory! Heed Sabine's words, when she cautions: "Actually, if you believe this idea, the quantum fluctuations still go on outside of our universe, so there are constantly other universes being created." Input: output. Multiple universes are the outcome of believing in inflationary theory, whether you know it or not. Everyone who does not believe in Jehovah, the God of the Bible, in one way or another, believes in unfounded, unscientific Inflationary theory. Good luck with that!
Our last word on Guth's Inflationary theory, is that it is wrong in conception, development and execution. Every part of the theory is without foundation, or empirical support. We can confidently say so, for the following reasons. The first part of the conversation we have already covered in detail. We know why, Guth is incorrect, when he states, "Inflation, is based on ideas coming out of particle physics, which tell us that our theories predict that at very high energies, there should actually exist forms of matter, which turn gravity on its head, and cause gravity to behave repulsively, instead of attractively." We know that his theory is filled with inconsistencies. Some cosmologists, claim that the high - in fact - infinite, energies and densities that existed at the Big Bang, where so, because, all the matter in the universe, was forced to fit into an infinitely small volume of space - a singularity: and that's why that singularity had such high temperatures and density. Remember, those are the conditions that the extrapolating backwards, of the expansion of the universe, that we see playing out in red-shifted galaxies, is supposed to produce! But now, Guth is telling that no! The matter of the universe wasn't all there at the beginning, only a gram, and the gram gave rise to all the rest. I have a strong feeling someone is smoking quite a few grams. The plethora of problems that arise from these inconsistencies include, if there was only a gram of matter, was that enough to create the high energies, that create the conditions for negative gravity? If Guths speculations are right then what happened to the mainstream view that all matter got more and more condensed as the expansion is extrapolated backwards? Shouldn't the narrative be that all matter was getting more and more condensed, but then at a certain threshold, all matter disappeared, and nothing but a gram of matter was left?
It is tempting to address the inconsistencies line-by-line. But that is wholly unnecessary, and a trap. The mere discussion of unscientific speculation is a victory for the theorists who create such unhinged concepts. The threshold for discussing the details of any theory is that the theory has proven to be in-line with known scientific laws and empirical data. In the absence of such evidence, we will not waste our time interrogating the validity of speculations we know are not valid, for they are a metaphysical "a priori speculation upon questions that are unanswerable to scientific observation, analysis, or experiment." Alan Guth's theory of Inflation, ticks all those boxes! So, in discussing the details of his theory, we are not debating the veracity of his suggestions, but merely showing that his speculation meets all the identifying marks of an unscientific work of metaphysical speculation.
Next, Guth talks of, "... using the physics of what particle physicists call Grand Unified Theories," to calculate how many doublings of the size of the universe were needed for the universe to reach its current proportions. The only problem is that we know, that there is no evidence that the different forces of the universe were ever unified. That is, such an assumption is unscientific. How did Hossenfelder put it: "How scientific is this idea? Well we have zero evidence that the forces were ever unified, and have equally good evidence, namely none, that the Inflation Field exists." So, any so-called calculations that are based on these debunked assumptions are not following the evidence based scientific method! People say the Christian fundamentalists are wrong for claiming that God created the universe in 6 24 hour periods. And, of course, such criticism is correct, for such notions have no foundation in the Biblical record. However, at least Christian fundamentalists alloted 144 hours to the exercise, Guth claims a similar feat took place in 0.00000000000000000000000000000000001 of a second: that's a decimal point, followed by 34 zeros and a 1 at the end. In that time Guth claims the universe doubled a hundred times, and through magical disappearing negative fields creating all the matter we see today. Here are his assertions in his own words for easy reference:
RLK: So, in this period of time, the whole universe as we known it, was created?
AG: Essentially, that's right. Uh, inflation is not a theory of the ultimate creation of the universe. In that, to start inflation, one needs a bit of matter: approximately a gram, it turns out. But, once you have this gram, inflation actually does describe how all the rest of the matter that we see, which of course, is vastly more than a gram, is created. Absolutely!
While, some scientists claim to understand how gravity works, nothing could be further from the truth, as many, including Sabine among many others, openly admit that there is something wrong with Einstein's theory of General Relativity, which is supposed to describe gravity through the effects of Space-time. They freely admit, that the theory does not explain everything, and has some huge gaps, that is why everyone is searching for a theory of Quantum Gravity. I will explain gravity in detail, a little later, suffice it to say, that for now, what we can say with certainty is that there is no such thing as a gravity field, and gravity does not, have a "negative contribution to the total energy of whatever system it's a part of." What's more there are no negative energies in the universe: not from gravity, not from dark energy, or from anything else! All such invoking of negative energies are Scientism, attempting to invoke the Ether. Recall, how before anyone understood how heat, caused disgregation - the excellent word coined by Clausius - Lavoisier appealed to an Ether with the same powers to describe how "Caloric," pushed the molecules or atoms apart and caused phase transitions: from solid to liquid and from liquid to gas? In the history of science, negative energies, have always been invoked when scientists had "no idea" how a certain effect happens. The examples go all the back to the beginning of scientific enquiry and description. Before Lavoisier, it was Becher and Priestley who invoked Phlogiston, for the very same reason. As it was then, so it is now: since scientists "have no idea how the universe began," they invoke negative energies, without a shred of evidence for their existence.
Kuhn addresses the elephant in the room,
Now, it sounds like we're getting something for nothing, because how can you have energy being created, when we know there's a very tight law of conservation of energy and matter?" Robert Lawrence Kuhn
Just like Lavoisier, waxed lyrical about the virtues of Caloric, all without any experimental proof, so Guth, goes into excruciating detail about Inflation theory. This feature - exhaustive descriptions that don't have explanatory power - is a tell-tale sign of a theory that is nothing but undercooked metaphysical speculation. Bjorn Ekeberg, explained this counter-intuitive fact in a debate about, "Where is Physics Going?" where Sabine was also a participant:
Understanding relies on explanation! And, the power of a theory, traditionally, lies in its power to explain something. And, when you look at the field of Physics and Cosmology, the way its developed over the last century, historically speaking, its become better and better at describing phenomena, with more precision, and detail and layers. But its also become poorer at explaining them, and I think this is part of the problem: that there's a lot of people, inside and outside the scientific community are finding the current paradigm wanting for something. Like, it doesn't explain very much" Bjorn Ekeberg
From Aristotle and his precise descriptions of the perfect Celestial spheres which guided the motions of all celestial objects, to all the others we have covered: all of them have one thing in common, they excel at description, but utterly fail at explanation! What is the difference? Descriptions are only ever fully articulated by their proposers, explanations are understood by all, and can be repeated by anyone who takes the time to study the subject. That's why we have the common saying, "If you can't explain it to a five year old, you don't understand it yourself." Once the mental framework for a new paradigm shift in knowledge becomes common knowledge, it creates a knowledge base that serves as the foundation of quick comprehension of the new discovery. So self-evident does the new knowledge become that it quickly loses its novelty, and people act as if it was always common knowledge. Great scholars of the past have also noted this dynamic:
All truth passes through three stages. First, it is ridiculed. Second, it is violently opposed. Third, it is accepted as being self-evident" Arthur Schopenhauer
We see the difference between metaphysical speculation and genuine scientific progress in two ways. The speculators always announce their theories fully fledged, and without a shred of evidence. For instance, when Aristotle gave all those details about how the universe worked, did he ever ponder how one man, could possibly put together all those details? When Lavoisier, described in detail how the Caloric worked, what evidence had he discovered experimentally to back up his theory? When Maxwell insisted that the dynamics of electromagnetic waves were due to the empty space they were traveling through, had he conducted any research that led him to that conclusion? So oblivious to the facts are Etherists, that even when they, themselves discover evidence, they reject it in favour of unfounded speculation. This was case with Joseph Priestley, who as one of the last believers in Phlogiston theory discovered the element oxygen, but refused to believe it was an element, instead sticking to his belief that there were only four elements and Phlogiston. Thus the man whose experiments proved oxygen existed, died believing instead that it was actually dephlogisticated air! Albert A. Michelson devised an experiment that was so ingenious, that the results were so definitive, that everyone should have readily accepted them. And, they did, all except the man who conducted the experiment, for according to PBS Space Time's Matt O'Dowd, Michelson went to the grave still believing in the luminiferous ether. Etherism is a disease. When confronted with evidence that contradicts their claims, etherists never see the light, instead they bury their heads in the sand, and look instead for patches to the quickly disintegrating theories. At the very beginning of this blog, I quoted Neil DeGrasse Tyson, who said
The history of … scientific discovery, is one where at any given moment, there’s a frontier. And there tends to be an urge for people, especially religious people to assert that across that boundary, into the unknown, lies the handiwork of god. This shows up a lot.... This over time has been described by philosophers as: ‘the god of the gaps.’ If that’s … where you’re going to put your god in this world, then god is an ever-receding pocket of scientific ignorance. If god is the mystery of the universe" Neil DeGrasse Tyson
However, if you are paying, and soon, even for those who are not paying attention, the plain truth will become impossible to ignore: it is not God who is an ever receding entity, but scientists who believe in ethers and their complex descriptions, instead of the scientific method, and its simple evidence based explanations. The second way you can tell etherists apart from true scientists is bravado! Scientism, the art of how to practice etherism, requires boldness - not of ideas, but of presenting your empty speculations with a sense of self-assured finality. Etherists don't say we have no idea, but we're trying to experiment to find the answers. Whereas scientists, may have bold guesses, which it is necessary to make, in order to test and either verify or falsify them as a means of making progress, but they also always approach science with a healthy dose of skepticism! Not etherists, remember how Alan Guth's Wikipedia profile ended?:
By 1983, Guth had published a paper describing how his supercooled universe scenario was not ideal, as the "triggering mechanism" to exit such a state would require "extreme fine tuning of parameters" and felt a more natural solution was required. However, this did not deter him from the belief that the universe expanded exponentially in a vacuum in its early lifetime" Alan Guth Article - Wikipedia
"This did not deter him from the belief that ...." It never does deter them. Evidence is not a factor in the minds of etherists, only their undying beliefs, their eternal "a priori speculation[s] upon questions that are unanswerable to scientific observation, analysis, or experiment," serve to guide their thinking. Contrast that with the healthy skepticism, that all true scientists and seekers of knowledge in general evince in the course of their researches:
The best and safest way of philosophizing seems to be, first to enquire diligently into the properties of things, and to establish those properties by experiences [experiments] and then to proceed slowly to hypotheses for the explanation of them. For hypotheses should be employed only in explaining the properties of things, but not assumed in determining them; unless so far as they may furnish experiments" Sir Isaac Newton
For this reason Newton's words about the difference between speculation and science, between etherism and observational data derived from empirical evidence, between descriptions of one's imagination and explanations of the nature of reality are now more relevant, than ever before!:
A man may imagine things that are false, but he can only understand things that are true, for if the things be false, the apprehension of them is not understanding" Sir Isaac Newton
What is the key difference between the two, precise descriptions and an understandable explanation? Since explanations are based on reality, once you gather evidence for their operation, you can create examples of the phenomenon at work as attested to by Newton. But descriptions of empty speculations never come with demonstrable examples. To try and apprehend what is spoken of, you can only employ imagination, never demonstration, since the phenomenon does not actually exist! Like the 'endless staircase.' Such objects fall into the class of optical illusions. You can only draw them, never build a model in the real world. Similarly Scientism, is always claiming to have models of the evolution of the universe that are created by supercomputers. They claim, they just inputted, the starting conditions according to the Big Bang, together with the laws of nature - mathematical and otherwise - and the computers spit out simulations that approximate the universe we see. This is a lie! There are no such models of a Big Bang universe that evolved over time, from a hot soup to what we see today. Instead anytime they offer 'simulations,' it turns out they are nothing but an artists impression of what their theories describe. Their artist's impressions, are nothing but optical illusions! When I wanted to prove the falsehood of a homogeneous universe, I created an interactive model that proved the point, beyond doubt. With all the computing power available to us today, why can't Scientism provide simple demonstrations of their claims. No. The truth is, descriptions, no matter how detailed, do not suffice as proof of metaphysical speculations, nor are they an aide to understanding. For that only evidence based explanations, and real world examples will do - as attested to by greatest scientist of all time, Sir Isaac Newton, himself.
The best way to understanding is a few good examplesSir Isaac Newton
We conclude this subheading about Hossenfelder's analysis of all cosmological theories, with Sabine's own concluding words on the matter. After, she had put all cosmological theories into two camps: the scientific one: "we have no idea how the universe began," and the unscientific second camp, which is based on rejecting the admission of ignorance, since you cannot publish cluelessness, nor form a career out of it. Sabine says of the second camp, "So, it's not how the currently most popular theories for the beginning of the universe work." In other words, all the most current popular theories of how the universe works are UNSCIENTIFIC! She then goes onto to list other categories of theories that are alternatives to the fluctuating Space-time of the Big Bang, including the idea of a cyclical universe, in which the universe goes into and out of existence over long stretches of time. However, none of that is of concern to us, since we have already established, that no matter which of the "currenly ... popular theories for the beginning of the universe," we are speaking of, it falls into the second camp of theories that are unscientific. I'd like to remind you of K. Dunnigan's words,
A statistician is a person who draws a mathematically precise line from an unwarranted assumption to a foregone conclusion" K Dunnigan
I re-quote these words, as a reminder of our approach. We will not be wasting time dealing with the mathematical line, if we can determine that at either end, it is connected to either, an "unwarranted assumption," or a "foregone conclusion," for neither of those constitute science! Instead, we will merely prove that the assumptions were unwarranted, or the conclusions foregone. In either case, the result can never be scientific, for the simple reasons that if the assumption is unwarranted, it means it is evidence-free, which is unscientific; and if the conclusion is foregone, again that is not scientific as it has skipped the necessary step of experiment! It is important to highlight, though it should be self-evident, that in the history of science, man's intuition has never been the guide for scientific progress. The whole point about science is that nature is counter-intuitive, thus to get to the bottom of how it operates, we need experiment and bold guesses to guide us. And, this is where most people get confused: what's the difference between experiment and bold guesses and speculation - they may ask. The difference, is that bold guesses guide the experiment, and experiment reinforces if we're on the right track, or whether we need to make adjustments. These two factors work interdependently to guide scientific progress. This is not the case with metaphysical speculation, because as we've learnt, such speculation is "unanswerable to scientific observation, analysis, or experiment." Now, you might say: what is "unanswerable to scientific observation, analysis, or experiment" are religious questions and trying to prove scientifically that God exists. This, is in fact, is the strong assertion made by Scientism. All agnostic or atheistic scientists try to sell the belief that God is unknowable scientifically. That everything can be explained without recourse to God as a creative agent. But that, as we will soon find out is not, what is metaphysical! What is metaphysical are the speculations of scientists, that only live in their imaginations and have no link to reality, whatsoever. By the time we finish this blog, you will have concrete, verifiable evidence to that effect. To the fact that Etherism is what constitutes metaphysics, and God and the proof of his existence are easily demonstrable scientific facts, backed up by an abundance of scientific evidence. In other words, proof that God created the universe, falls within the realm of scientific evidence, whilst all theories that renounce God as the creator fall into the realm of metaphysical speculations.
As surprising as that may sound, that is what we will prove! The reason all current popular theories about the origin of the universe fall under the umbrella of unscientific theories, is that they all deviate from the empirical evidence as provided by the CMB. I will say it again, because the point is that important: everything we know about the universe, we have learned through light! As such anyone who goes against, the evidence of the light, whether that light is stellar light, red-shifted galactic light, thermal spectra, or the earliest light to ever exist - the CMB, is immaterial. If we want to know about the universe, we have to study and critically accept, the evidence that light gives us. The evidence of the CMB is that the early universe was in a "rather special state," where the matter and light were at the same temperature and the entropy of gravity was zero, that is, the universe was at critical density: the curvature of Space was flat. Those are all different ways of saying the same thing. To understand the dynamics of that early stage of the universe we have to understand what that empirical evidence is telling us: and to do that we only need to consult the laws of thermodynamics, the ideal gas law, and the laws of gravity.
Recall that the are Two Realms in the Universe!
Of course, we are not at a complete dead end, for we know that there is more than one kind of REALM, in the universe. If not baryonic, then the deadlock had to be broken by Dark Matter. More interesting yet, we realize that according to the laws of thermodynamics, for a baryonic system to be susceptible to inputs from its surroundings, tells us one of two things about the relationship between itself and its surroundings. If there is a transference of energy between the two, then the system receiving the energy is a close system. If it can also receive matter, then the two systems form an 'open system.' However, if no energy, or matter can cross the boundary, then the system is an isolated system. From this analysis, we know that since, the universe's "special state," was thermodynamically deadlocked, at a time when there was very little matter in the actual universe, we know that the it must have received a form of energy that originated in the Dark Matter realm of the universe, hence the universe and its baryonic and dark matter realms form at a minimum, a closed system! Having debunked the existence of dark energy, long ago, let us not confuse that with the energy from a the dark matter realm. These are two completely different things, though bad nomenclature from the scientific community confuses the issue.
There's more. Since,
4. Strangely Partitioned Entropy
What makes the entropy partition strange? Firstly, let's remind ourselves of what the partition is between. Steinhardt, tells us that the entropy between matter and radiation (light), is maximal because they are at the same temperature, which we understand. Now he continues:
... Whereas, the geometry, the space-time, the gravity, is nearly perfectly uniform, so almost no entropy." Paul Steinhardt
It's unfortunate that we always, have to correct the statements of scientists, who are supposed to be the most precise communicators, but are always speaking ambiguously, so as to leave wiggle room for any later revisions of their theories. Here, Steinhardt says, "the geometry ... the gravity, is nearly perfectly uniform, so almost no entropy." Of course that is not true: gravity was precisely perfectly uniform, there was in fact no entropy - gravitationally. We know that because, by their own admission the critical density, of the universe as reflected in the CMB is calculated to being within 1 part in 1062 or less, of critical density. That number 1 part in 1062, is accuracy beyond all human comprehension. Deviating by 1 part in 10 or less, means its more than 90% accurate. Deviating by less than 1 part in 100, means it more than 99% of the target figure. Deviating from exact critical density by less than 1 part in 1062, is a number with a 1, that's followed by 62 zeros! Here's what that looks like:
100,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
No human can even fathom how small a deviation 1 over that number would represent, because none of us can relate or understand a number that large. And, again, this deviation does not represent reality, but the limitations of our measuring devices! So, for all intents and purposes, the CMB data tells us that the the geometry of the universe was exactly at critical density. We continue.
Matter and radiation are at maximal entropy, by definition of the fact that they are at the same temperature, while gravity and geometry is at minimal entropy, because it is at Critical Density. To understand what is going on here, we have to ask ourselves a question that we have not confronted before: what is Space? What do we mean when we speak about Space? Before, we ask that uncomfortable question, we will not be able to make heads or tails of what is actually going on, for the simple reason that, without knowing that answer, we cannot hope to understand gravity, or how so-called space-time operates. For instance, when we speak of Critical Density, how many entities are involved in the calculation, and what are they? We are familiar with the concept of critical density, and we know that at the least baryonic matter is one of the entities involved, but what about Space itself? Is Space made up of baryonic components, or of something else? Also, how does dark matter fit into the picture? How does the scaffolding of the universe, factor into these discussions?
A big problem comes from confusion among scientists themselves as to the nature of Space. Even a shallow review of Einstein's theory of general relativity about gravity being an effect caused by the curvature of space-time is quickly proven to be false. For one thing, Einstein, characterized gravity as a form of accelerated motion that caused the sensation of being pulled down into the earth. And it is this sensation, that we label - gravity. This is nonsensical, on the face of it. Two people who are on opposites sides of the earth, say one is on the south pole and the other on the north pole, both feel the pull of gravity. According to Einstein, this is not because the earth is pulling down on them through some force, that Newton quantified, but was unable to identify the carrier agent of. No, says Einstein! What is actually happening is that the earth, is simultaneously, accelerating upwards underneath both individuals, and it is this 'upward acceleration,' that pushes us into the surface of the earth, causing the sensation of being pulled towards the center of the earth. This is obviously wholly incorrect, for otherwise, the earth, continually accelerating outwards in all directions, would have to expand radially, to keep the effect up. As the size of the earth is not growing outward, in all directions by 9.8m per second - the speed of gravity on earth! Einstein is also wrong, because subatomic particles gravitate, but there is no theory of quantum gravity, that is, of how subatomic particles gravitate. Since, Einstein's theory does not agree with observable facts, and is inadequate in explaining reality, the explanation for gravity, must come from another quarter.
Another gaping whole in the Big Bang cosmologists theories comes from how they insist that the universe expands. This is demonstrably false. It is true that the universe, has increased in dimensions, but the universe is not and has never expanded in all directions, and in all places, as has long been the claim. Again, the dissenting voice belongs to the Albert Einstein Professor of Science at Princeton University, Paul Steinhardt - I quote:
If the Big Bang, were an explosion - think about what happens when you have an ordinary explosion. First of all, there's going to be a center to that explosion. And, you're gonna know there's a center to that explosion because, as everything leaves the center of the explosion, things which are more massive, are not going to travel as far as the things that are less massive.... If you believe that was true of he Big Bang, we should find that massive galaxies, are traveling more slowly than less massive galaxies.... It turns out the motion of galaxies doesn't depend upon their mass at all! Their apparent motion only depends upon how far away they are. So what's really a better picture of what you're talking about is Space stretching. So, if Space is stretching uniformly, what's in that Space, whether it's massive or not massive, moves away from us - due to the stretching - by the same amount.... That's actually what we observe. That's what Hubble observed. He observed that distant galaxies - doesn't depend upon their mass, but - depending upon their distance, seem to have a recessional speed - a speed away from us - that's proportional to their distance: that corresponds to a stretch!" Paul Steinhardt
I reiterate that as a scientist, Steinhardt will always colour the observational data with his believe in the Big Bang, you have to be nuanced enough to start discerning for yourself, what is empirical data in his statement and what is speculative theory, for otherwise the blog would never end, if I were to always correct every scientist who makes a statement. But, to be just, Steinhardt really does seem to be trying harder than any of his contemporaries to find the truth, behind reality. You can see that whenever he spots an inconsistency in how people understand the data, he exposes the wrong thinking. In this case, its understanding what the empirical data is telling us about the nature of the growth of the universe. If the growth were due to an inflationary explosion, then more massive objects, such galactic super-clusters would travel more slowly, than lighter masses. However, what determines the speed at which galaxies are moving away from the earth, in all directions, is not their size but their distance away from us. That means Space is being stretched, not and the velocity of the matter depends on the which region of Space, it finds itself embedded in. Put another way, all regions of Space that are an equal distance away from the earth are moving at the same speed. That could not happen if Space were a medium that filled all locations in the universe simultaneously. For then, not only would the galaxies be moving away from the earth, but internally, the different objects within a galaxy would be moving apart from each other. And, that's not what we see.
